Abstract
This study assessed the systems thinking skills–consisting of seven constructs–of undergraduate students in a food-energy-water nexus module. The module featured a four-part assignment using a data visualization tool, Hydroviz, to analyze food, energy, and water data in a U.S. region and address a socio-hydrologic challenge. The research questions were (1) what systems thinking constructs were students able to engage in most effectively?, (2) in what ways do students’ tasks with higher and lower systems thinking scores differ?, and (3) what factors (e.g., conceptual understanding, socio-scientific reasoning, demographics, curricular resources, and Hydroviz) support students’ systems thinking outcomes? Data from n = 94 students included demographics, pre-assessments and assignments, and interviews with 13 students. Results showed moderate enaction of systems thinking skills, with students emphasizing problem framing and goal setting, and prioritizing technical over contextual aspects. Curricular resources effectively supported data exploration, system connections, leveraging prior knowledge, and identifying management solutions.
License
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Article Type: Research Article
INTERDISCIP J ENV SCI ED, Volume 21, Issue 2, 2025, Article No: e2506
https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901
Publication date: 01 Apr 2025
Online publication date: 29 Jan 2025
Article Views: 620
Article Downloads: 316
Open Access HTML Content Download XML References How to cite this articleHTML Content
INTRODUCTION
Socio-scientific issues represent complex challenges that integrate scientific and non-scientific dimensions, including ethical, moral, and affective considerations (Sadler et al., 2007). Their scientific dimensions require the application of scientific principles, methods, and knowledge to comprehend and address the problem, while the non-scientific dimensions encompass a wide range of social, ethical, moral, and affective aspects. These problems can be considered wicked problems (Rittel & Webber, 1973), as well as sustainability concerns. Among socio-scientific issues, socio-hydrologic issues focus on water resource challenges. The food-energy-water (FEW) nexus represents one subset, highlighting the interconnectedness of water, energy, and food systems. It involves multiple disciplines, stakeholders, and sectors interacting together across different scales to shape water management strategies (Food and Agriculture Organization [FAO], 2014; Wade et al., 2020). Managing interactions within the FEW nexus requires a holistic approach, integrating diverse disciplines and sectors (FAO, 2014; Wade et al., 2020). This approach fosters the development of practical solutions, science-based policies, and research that supports decision-making in areas such as infrastructure planning, climate change adaptation, and water governance (FAO, 2014).
Systems thinking is a key competence for undergraduate students to address socio-hydrologic issues, like those taking place in the FEW nexus. It involves a comprehensive analysis across domains and disciplines, fostering a holistic perspective of the issue (Davidson et al., 2021; Grohs et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Platts et al., 2022; Redman & Wiek, 2021; Scherer et al., 2017). However, limited research exists on instructional approaches supporting students’ systems thinking skills in relation to socio-hydrologic issues, or other complex issues (Gilbert et al., 2019; Grohs et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Liu, 2022; Scherer et al., 2017), particularly in online environments (Davidson et al., 2021). The authors evaluate undergraduate students’ systems thinking skills–consisting of seven constructs–within a decision-making assignment focused on an authentic FEW nexus case, using a web-based data visualization tool–Hydroviz. The research questions are, as follows:
-
What systems thinking constructs were students able to engage in most effectively?
-
In what ways do students’ tasks with higher and lower systems thinking scores differ?
-
What factors (e.g., conceptual understanding, socio-scientific reasoning (SSR), demographics, the curricular resources, Hydroviz) support students’ systems thinking outcomes?
Findings will inform the development of instructional strategies for enhancing systems thinking skills in socio-hydrologic issues.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Undergraduate Education About Socio-Hydrologic Issues and Other Socio-Scientific Issues
Diverse teaching approaches have been implemented to engage undergraduate students in evaluating authentic socio-scientific issues (i.e., Gilbert et al., 2019; Grohs et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2010; Tsai & Liu, 2022). Studies focused on socio-hydrologic issues have foregrounded the use of authentic cases such as water pollution from agricultural activities (Lally & Forbes, 2020; Owens et al., 2020) and oil spills (Forbes et al., 2018; White et al., 2021), as well as water resource allocation for agriculture considering climate-related factors (Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Lally et al., 2020; Liu, 2022; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; Sabel et al., 2017), population growth (Bajzelj et al., 2016), ocean health (Gilbert et al., 2019), and hydraulic fracturing (Romine et al., 2017), among others. These cases aimed to enhance students’ understanding and reasoning regarding the complexities about socio-scientific issues.
Across these experiences, different areas of students’ learning have been evaluated. Some studies focused on evaluating SSR (Owens et al., 2020; Romine et al., 2017; Tsai & Liu, 2022); decision-making (Lally & Forbes, 2020; Lally et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2010; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2024; Sabel et al., 2017); modeling (Bajzelj et al., 2016; Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Lally et al., 2020; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; White et al., 2021); and spatial thinking (White et al., 2021). These studies suggest that engagement with socio-scientific issues allowed students to provide more sophisticated reasoning about stakeholders’ perspectives (Liu et al., 2010; Owens et al., 2020; Romine et al., 2017) and enhance their conceptual understanding of hydrologic concepts (Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Liu, 2022).
Undergraduate Education About Systems Thinking Within the Context of Socio-Scientific Issues
In a systematic literature review by Scherer et al. (2017), four groupings were identified to organize studies on students’ systems thinking skills within Earth’s systems. Two of these groupings focus on understanding how students apply systems thinking to understand the connections between human and natural systems from an ‘Earth systems perspective’–which focuses on the interactions between humans and decision-making–and ‘authentic complex Earth and environmental systems’–which focuses on the connection between environmental systems and human activities and decision-making in a highly contextualized approach. The other two groupings, ‘Earth systems thinking skills’ and ‘complexity sciences’ emphasize the interconnected Earth systems and draw directly from complexity sciences, respectively. The former two better align with the study’s focus.
Various pedagogical approaches and educational programs have been developed to afford students opportunities to evaluate authentic cases and understand the interrelations between systems, using modelling and visualization tools (Bajzelj et al., 2016; Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Lally et al., 2020; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; White et al., 2021), written articles (Lally & Forbes, 2020), board games (Tsai & Liu, 2022), and discussions on policy impacts on climate change (Gilbert et al., 2019). Through these experiences, students identify and comprehend interactions between human and natural systems, enabling them to conduct complex analyses, predict outcomes, model system changes, and recognize factors influencing system alterations (Bajzelj et al., 2016; Forbes et al., 2018; Gilbert et al., 2019; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; Tsai & Liu, 2022; White et al., 2021). They also showed that students may experience difficulties in critically evaluating information sources (Owens et al., 2020) and providing accurate supporting information (Sabel et al., 2017). While some research shows that science majors based their decisions from a disciplinary approach (Liu et al., 2010), other studies observed no significant differences between students from STEM and non-STEM majors (Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022).
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Understanding how human and environmental systems interact is crucial for decision-making regarding complex issues, including socio-hydrologic issues (Grohs et al., 2018; National Research Council [NRC], 2005). This involves addressing such issues from multiple disciplinary perspectives, ranging from multi-disciplinary approaches, which focus on specific aspects within disciplinary boundaries, to inter-disciplinary approaches, which provide a broader perspective from various coordinated disciplinary angles, and finally, transdisciplinary approaches, which offer comprehensive and holistic strategies to tackle problems in their entirety (Choi & Pak, 2006). Consequently, the integration of systems thinking varies across these approaches. Numerous frameworks exist to assess students’ systems thinking skills. Here, the authors’ aim is to evaluate these skills from an authentic complex Earth and environmental system perspective (Scherer et al., 2017). Within this scope, Grohs et al. (2018) developed a framework to encapsulate various dimensions of systems thinking skills essential for addressing challenges requiring collaboration across disciplines. In this framework, systems thinking is conceptualized as a metacognitive strategy involving ‘a flexible way of framing, reasoning, and acting within multiple dimensions’ (Grohs et al., 2018 p. 111). These dimensions include
-
understanding the problem, encompassing technical and contextual aspects;
-
considering perspectives from multiple stakeholders and their influence on the problem and its solution; and
-
temporal aspects, involving reflection and prediction within the problem-solving process (Grohs et al., 2018).
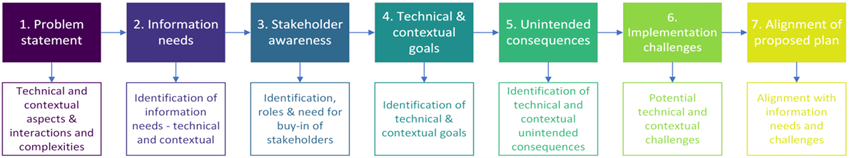
Grohs et al. (2018) developed an assessment tool with seven constructs and operational definitions (Figure 1) to capture these dimensions and evaluate students’ use of systems thinking skills as they addressed a socio-scientific issue related to the impacts of energy costs. Lally and Forbes (2020) and Liu (2022) adapted the framework to evaluate students’ use of systems thinking skills considering other socio-hydrologic issues.
METHODS
Research Context
Between 2017 and 2021, an undergraduate course was offered each spring at a research-intensive university (university 1)–or R1 university–in the Midwestern United States. This course welcomed students from both STEM and non-STEM majors. It provided opportunities to explore diverse modeling tools for evaluating the uses of and impacts on surface and groundwater resources resulting from various human activities. Additionally, students engaged in applying their systems thinking skills and participating in decision-making processes to address authentic issues (Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Lally et al., 2020; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2024; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; Owens et al., 2020; White et al., 2021). In 2020 and 2021, as part of a four-year project collaboration between university 1 and another R1 university in the Southern United States (university 2), a three-week curriculum module was developed, tested, refined, and implemented at university 1 (Mostacedo-Marasovic & Forbes, 2024). This module was subsequently shared with undergraduate instructors in 2022 and 2023 (Mostacedo-Marasovic & Forbes, 2024). The study focuses on the second year of implementation of the module in 2021, during which the course was conducted asynchronously due to the COVID-19 pandemic (Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022). The course comprised eight modules spread over 15 weeks, with the FEW nexus being the focus of the fourth module covered between weeks four and six (Table 1).
Table 1. Course’s modules
|
Features of Hydroviz
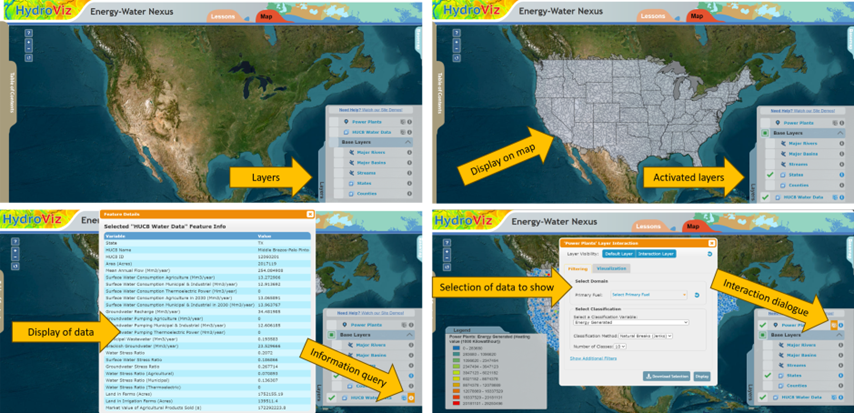
Hydroviz, developed at university 2, is tailored for hydrology education, offering students access to in situ data and simulations to enhance their understanding of hydrologic concepts and develop observational and data analysis skills (Habib et al., 2012). This web-based data visualization tool uses real data from the United States, covering surface water flow, groundwater recharge, water consumption and stress ratio, and energy production (Habib et al., 2012). After its initial design, Hydroviz later incorporated data on agricultural production. The water and agriculture data are organized at a subbasin level designated by the United States geological survey as hydrologic unit codes (HUC) 8 (Habib et al., 2012) (Figure 2). Hydroviz allows students to interact with a map of the country, offering seven layers of information for each subbasin. These layers include power plants, water, and agricultural data categorized by subbasins, major rivers, major basins, streams, states, and counties. Through interaction dialogues, students can activate, re-organize, and explore these layers, allowing them to identify variables of interest, visualize data on the map, apply classification and filters for data comparisons across different locations, and download the data as “.csv” files.
The Food-Energy-Water Nexus Module
The FEW nexus module, taught in 2020 and 2021, aimed to equip students with the ability to
-
describe the components and socio-economic and environmental importance of the FEW nexus,
-
analyze real data concerning different systems within the FEW nexus, and
-
engage in evidence-based decision-making regarding the FEW nexus.
Structured into four main units, this module fostered an understanding of global and national perspectives regarding the FEW nexus. The first unit, the introduction to the FEW nexus, acquainted students with the FEW nexus components, the HUC classification system, and the use of Hydroviz, which they began utilizing for the initial part of the assignment. The second unit, focusing on the water-food nexus, explored global and local irrigation practices while continuing work on the assignment’s second part. In the third unit, water-energy and food-energy nexus, students delved into the relationships between water and energy for energy and water production, respectively, and they continued with the third part of the assignment. Finally, the decision-making unit introduced students to a systematic decision-making process, employing fictional scenarios (e.g., pet adoption or addressing a socio-hydrologic issue) to familiarize them with the process’ application. Later, they engaged in the fourth part of the assignment to address the case. The module, titled “food-energy-water nexus”, is accessible on the HydroLearn website by [university 1].
Decision-Making Assignment (The Assignment)
As part of the module, students completed a four-part assignment using Hydroviz and guided questions to analyze collected data. They assumed a role as members of a public energy utility, tasked with recommending the implementation of a new energy matrix in a chosen United States region. In part I, students were introduced to the case and used Hydroviz to gather and analyze data on food, energy, and water-related variables in the region, including, water availability and stress, energy generation, and agriculture production. In part II, students continued using Hydroviz and supplemented it with data from the census of agriculture (USDA–NASS, 2018) to further investigate water use for agriculture, monetary value of agricultural production, types of commodities produced, and associated water, land, and carbon footprints. Part III involved a deeper exploration of the relationship between water and energy production, including water and land footprints associated with energy production and energy production costs. In part IV, students engaged in decision-making, identifying the problem, setting objectives and evaluation criteria, proposing alternative solutions for the new energy matrix, evaluating consequences and trade-offs, making a decision, and analyzing it to identify additional considerations. Appendix A provides examples of questions from each part of the assignment.
Data Collection and Sources
At the course’s start, students were given a consent form approved by university 1’s Institutional Review Board to participate in the research. Data was collected from n = 94 students who participated in the second iteration of the FEW Nexus module and provided consent. The collected data included
-
demographic information such as gender, major, and academic level,
-
a pre- and post-assessments,
-
responses to the assignment, and
-
transcripts from interviews conducted with n = 13 students.
A summary of the students’ demographics is provided in Table 2.
Table 2. Summary of students’ demographics
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pre-assessment
This instrument served as a baseline assessment and comprised three sections to evaluate students’ prior knowledge at the beginning of the course. The first section contained 32 multiple-choice and 9 open-ended questions about water resources. Multiple-choice questions were assigned 1 or 2 points based on difficulty, while open-ended questions were worth 2 to 5 points, yielding a maximum score of 76 points. The second section included 24 true or false statements about the FEW nexus, with each correct response earning 1 point, for a maximum score of 24 points. The third section presented a brief case on the construction of a corn ethanol plant for biofuel in an economically depressed area. It encompassed 2 multiple-choice questions, and 10 open-ended questions designed to evaluate students’ SSR. SSR evaluates students’ abilities to assess socio-hydrologic issues, understand stakeholders’ perspectives, emphasize ongoing inquiry, and articulate arguments (Owens et al., 2020; Romine et al., 2017; Sadler et al., 2007). Open-ended questions were evaluated by two reviewers, with a maximum score of 20 points.
Parts I, II, and III of the assignment
In each part, students collected data and performed calculations to address questions regarding their chosen region. The authors ensured that each student completed all responses for course evaluation purposes. However, for the study, the authors did not assess these responses. Evaluating them would have necessitated scrutinizing data for accuracy across selected regions for each student, which did not align with our research questions. Instead, authors utilized the interviews to assess how these parts contributed to students’ understanding of the FEW nexus in their region.
Part IV of the assignment
Part IV comprised 20 open-ended questions focused on the decision-making task. For research purposes, the authors used a scoring rubric developed by Grohs et al. (2018) and adapted by Lally and Forbes (2020) to evaluate how students assessed each systems thinking construct (problem statement, information needs, stakeholder awareness, technical and contextual goals, unintended consequences, implementation challenges, and alignment of proposed plan) (Appendix B). The scoring rubric was different than the one used to assess students’ assignments for grading. It was developed following an iterative and systematic approach involving multiple raters (Grohs et al., 2018). To maintain consistency with previous methodologies (Grohs et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020), the authors summed the scores of the seven constructs, each ranging from 0 to 3 points. This summation yielded a total systems thinking score ranging from 0 to 21 points. Inter-rater reliability between two reviewers was evaluated. Following four rounds of evaluation and revision, joint assessment was conducted on 20% of the assignments. Initial agreement reached 71%, progressively increasing to 89%, 86%, and finally 91% after subsequent rounds of review and discussion. Cohen’s kappa (k = 0.81) calculated after the final coding round indicated near-perfect agreement. Subsequently, a single reviewer assessed the remaining assignments using the rubric.
Interviews
The interviews aimed to explore how each part of the assignment contributed to students’ observation and analysis of the FEW nexus. The authors devised an interview protocol comprising 5 sections covering students’ involvement with each of the four assignment parts and their interaction with Hydroviz (Appendix C). All students were invited to participate in individual interviews. Interviews lasted between 15 to 30 minutes, maintaining the order of questions, and were conducted by two co-authors of the study. Students were assured that their participation in the interviews would not impact their course grade and received a $20 study subject stipend.
Data Analyses
The authors employed both quantitative and qualitative approaches for data analysis (Figure 3). To address the research question “what systems thinking constructs were students able to engage in most effectively?”, using part IV of the assignment, the authors conducted a non-parametric Friedman test to compare each systems thinking construct. Post-hoc analysis was performed using Wilcoxon tests.
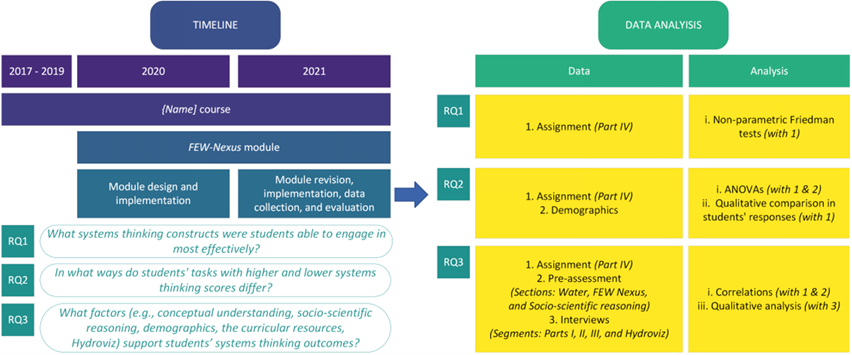
To address research question 2, “in what ways do students’ tasks with higher and lower systems thinking scores differ?”, using data from part IV of the assignment, the authors used analyses of variance (ANOVA) to compare differences between students’ demographics (academic level, gender, academic field, place of residence, and nationality) and their total systems thinking scores, as well as each of its constructs. Additionally, the authors conducted a qualitative analysis of students’ responses to part IV of the assignment to discern differences between high and low systems thinking scores for each construct.
To address research question 3, “what factors support students’ systems thinking outcomes?”, the authors obtained correlations between each demographic variable and each segment of the pre-assessment with the total systems thinking score. These correlations informed the construction of a regression model to assess whether any variables could predict students’ systems thinking scores. However, upon identifying statistically significant correlations, the authors observed that the parameters did not meet the assumptions of constant variance and normality required for the regression model. Despite attempts to address this issue through transformations, the parameters of the linear regression remained unreliable. Consequently, only the correlations found are reported.
The authors conducted a qualitative analysis of the interviews to examine how Hydroviz and the learning activities potentially contributed to students’ systems thinking outcomes in parts I, II, and III of the assignment. Responses were organized in an Excel matrix and initially coded based on their focus (food, energy, or water; food-energy, energy-water; food-energy-water; Hydroviz). Subsequently, employing open coding, five themes that characterized students’ responses were identified (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016). These themes are elaborated upon in the results section.
RESULTS
RQ1. What Systems Thinking Constructs Were Students Able to Engage in Most Effectively?
The findings indicated a moderate level of proficiency in students’ systems thinking skills, with a mean score of 68.52% and a standard deviation of 16.38% of the systems thinking total score. Students demonstrated better proficiency in evaluating systems thinking constructs that contribute to the main framing of their analysis (problem statement, technical and contextual goals, and alignment of proposed plan) compared to constructs focusing on the finer details of the analysis (information needs, stakeholder awareness, unintended consequences, and implementation challenges). The Friedman test of systems thinking constructs X2 (6, n = 94) = 136.04, p < .0001 and post-hoc tests (Wilcoxon test), confirmed these differences (Figure 4). Specifically, problem statement (mean [M] = 2.21, standard deviation [SD] = 0.78) scored higher than stakeholder awareness (M = 1.80, SD = 0.82), unintended consequences (M = 1.76, SD = 0.84) and implementation challenges (M = 1.68, SD = 0.77). Similarly, technical, and contextual goals (M = 2.37, SD = 0.70) scored higher than information needs (M = 1.86, SD = 0.84), stakeholder awareness, unintended consequences, and implementation challenges. Alignment (M = 2.63, SD = 0.69) scored higher than all the other constructs except for technical and contextual goals. See Table 3 for descriptive statistics, and Table 4 for post-hoc tests results. These trends were consistent for all subgroups of students. Results from the ANOVA for demographic variables (gender, major, academic level, residence, and nationality) showed no statistically significant differences for the systems thinking score or its constructs (Appendix D).
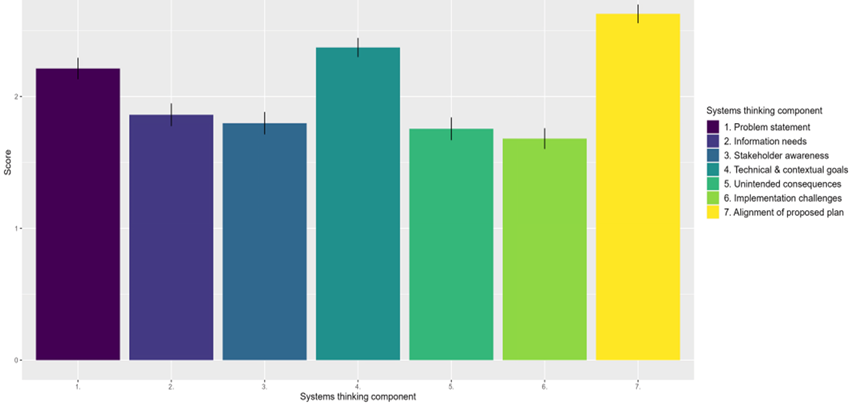
Table 3. Systems thinking total scores and constructs’ descriptive statistics
|
Table 4. Systems thinking post-hoc tests
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RQ2. In What Ways Do Students’ Tasks With Higher and Lower Systems Thinking Scores Differ?
Framing of the problem and goals
Students with higher systems thinking scores offered comprehensive justifications of the aspects that led to the decision to change the energy matrix, considering both technical aspects and the community’s significance. A student replied:
“Converting 1,420,904 MWh of natural resource-based energy into renewable energy sources while limiting environmental impacts has its challenges. There will be a loss of jobs, possible loss of land and natural habitat when land is converted for renewable energy yet [it] will reduce environmental degradation, greenhouse gases and water pollution” (part IV 24144).
Moreover, these students articulated a diverse range of goals encompassing technical factors (energy costs, reliability, and affordability), and contextual considerations (economic impact, environmental health, and community well-being). A student responded:
“[The main goal is to] build a power plant that will reduce costs while increasing the efficiency of land use and water quality and availability. The most important is reducing costs and environmental degradation. I care about the development of [the city]” (part IV 2493).
Conversely, students with lower scores tended to provide more generalized justifications for adopting a new energy matrix and their goals were either more generic or solely focused on technical aspects. A student described:
“I need to figure out how to get cleaner energy produced. [The public utility] still needs power and I need to reduce the number of fossil fuel plants. I need to minimize the fossil fuel footprints, while also keeping the same megawatt hours” (part IV 573).
Development of information needs, stakeholder awareness, unintended consequences, and implementation challenges
Students with higher systems thinking scores demonstrated a stronger ability to identify additional information required to assess the case thoroughly. They highlighted various technical needs such as energy demand and supply forecasts, construction and maintenance costs, alongside contextual considerations including job impacts, environmental and economic effects, and stakeholder perspectives. Some needs a student provided included:
“Additional data I would like would be estimates of project prices, so I can judge how much taxpayers would be spending; how much money could be saved by trying to transition fossil fuel plants into clean energy plants, so I can see how much money taxpayers would have to spend” (part IV 87102).
Their analysis of unintended consequences and implementation challenges reflected a balanced consideration of technical and contextual aspects. A student said:
“Nuclear is probably not liked very much by the public and so [it] would take a lot of [public relations] and marketing to convince people to allow a nuclear power plant to be built” (part IV 4058).
Conversely, students with lower systems thinking scores displayed more limited identification of information needs, providing brief explanations of relevance. A student responded,
“[I would need more information about] the lifespan of each option. This would be helpful because if something doesn’t last for a long time it might not be the best option even if it does meet the other criteria” (part IV 517).
Their stakeholder analyses were limited to listing the stakeholders and, in some cases, briefly describing their concerns. A student responded,
“The [public utility] officials would care about energy. Civilians will care about if their taxes go up. Environmentalists would care if it would harm the environment” (part IV 0599).
Similarly, the descriptions of unintended consequences and implementation challenges tended to focus on technical aspects, lacking depth in contextual considerations. For wind energy, solar and hydroelectric power, several technical consequences included
“high energy production and environmental protection ... [However], wind turbines can take up large land area and they can be expensive” (part IV 2362).
Alignment of proposed plan
Students with high scores demonstrated a strong alignment throughout their analysis, ensuring that their final decision resonated with the identified problem and main objectives. Conversely, students with low scores exhibited gaps between their final selection and the identified problem and goals in their analysis.
RQ3. What Factors Support Students’ Systems Thinking Outcomes?
The authors found a positive correlation between the systems thinking and SSR pre-scores, r (94) = 0.368, p = .0003. No other correlations were statistically significant (Appendix E). However, how predictive these SSR scores are of students’ systems thinking skills requires further analysis.
Engagement with Hydroviz and parts I, II, and III of the assignment facilitated students’ understanding of the FEW nexus in their region. This enabled them to
-
explore data on food, energy, and water in their selected region,
-
recognize interconnections between these systems,
-
connect with their prior learning and modify assumptions,
-
identify resource management challenges, and
-
reflect on management alternatives to address these challenges.
Data exploration about the FEW–Nexus
Hydroviz allowed data access and visualization, consolidating information into a single platform and minimizing the effort needed to gather data from multiple sources. Guided by specific questions, students used Hydroviz to collect and evaluate data on surface and groundwater availability, as well as water usage across different sectors within sub-basins, noting variations even among neighboring areas. A student commented:
“I worked with [subbasins 1, 2, and 3], and they had similar [water-related] data, which was kind of interesting to analyze, but [subbasin 3] had a lot larger, which makes sense, it is a larger source, and it provides for a larger area” (interview S04 L82).
Students used the resources to analyze the distribution of energy sources and their production levels in their region. They noted differences between regions and investigated potential reasons behind these variations. Additionally, students recognized that the characteristics of the same energy sources could vary based on geographical location. A student said:
“I thought [it] was interesting how wide of an area the power is generated in ..., and then also how diverse the different sources of power were like. There were biofuels and then traditional oil and coal, and then solar” (interview S10 L61).
Students examined various crops and animal products in their region. They also analyzed the monetary value of agricultural output and the use of resources such as land, irrigated areas, and input prices. A student indicated:
“From the graphs, I thought the food crops were planted on a bigger land, but it is different, because beef herd, cheese, cover a bigger area in my region. I thought things like potatoes, fruit, tomatoes, and wheat covered the biggest land in agriculture, but it is not the case” (interview S09 L102).
Connections between systems
Students explored the interconnections among the three systems in their regions, leveraging Hydroviz to examine agricultural water usage, and its reliance on surface and groundwater for irrigation, acknowledging its economic significance. They extended this insight to infer potential scenarios in other regions. A student commented:
“It ... seemed like they used way more groundwater for irrigation, even though, in my region anyways, [it] seemed to have way more surface water than groundwater” (interview S02 L137).
Recognizing the importance of water and energy, students evaluated how different energy sources use varying amounts of water and have distinct environmental impacts. They assessed the preference for surface or groundwater usage, considering geographical influences. For instance, they noted the substantial water demands associated with coal production and hydroelectric power, elucidating connections that may not have been immediately apparent. A student commented:
“In part three, I learned how much water connects to everything, especially energy. Before maybe I thought what the use could be with hydroelectric power, but I learned that water is used in so many forms of energy, not only hydroelectric power” (interview S03 L131).
Students expressed a need for additional contextual information, such as biodiversity and irrigation systems, and more technical details regarding water usage for different energy sources. A student indicated:
“My main source of energy in my region is natural gas and I don’t know enough to know if water after it is used for natural gas comes out clean and is reusable, or if it is heavily polluted. I would need more information to truly decide if it was sustainable” (interview S02 L272).
Connections with prior learning and assumptions
Students brought varying levels of knowledge and experience to the task, ranging from familial involvement in agriculture to formal education in college, practical experience in the energy sector, or no prior exposure at all. This diversity enabled students to leverage their existing knowledge when tackling the tasks. For example, in a prior unit, students learned about climate zones and their relationship with agriculture production. A student indicated:
“I noticed that there was a lot more water used in the [region]… which is sort of [to the] Northwest and used by far the most surface water for agriculture, as well as groundwater. So, I guess that sort of fits with the climate zones of [state], how farther west you go the drier” (interview S10 L114).
Access to numerical values allowed students to grasp the scale of analyzed variables, prompting students to reassess assumptions about water usage in their regions and recognize prior inaccuracies regarding energy sources. A student said:
“When I answered [about] what percent of water available is surface water and groundwater, I had about 60% more surface water, which was kind of surprising to me just because [the state] has the aquifer. I figured groundwater would be kind of more ... That opened my eyes a little bit” (interview S07 L49).
Potential resource management challenges
In certain regions, students noted insufficient water availability to meet consumption needs, with certain uses exceeding initial expectations, prompting a call for necessary changes. They also observed variations in water requirements among different agricultural products, highlighting the strain on groundwater and surface resources, particularly in relation to existing irrigation systems. Similar observations were made regarding different energy sources’ varying water resource demands. This facilitated an assessment of water resource sustainability. A student indicated:
“In this region, they produce corn, pigs, and some cows. I found most water is used in animal production than in crops. This for me was a problem because if the animals consume most of the water and people eat meat in this region, the water sources are in danger” (interview S08 L108).
Management of alternatives to improve water use efficiency
As students connected these systems, they weighed the importance of balancing environmental and economic concerns. Students brainstormed strategies to improve water use efficiency, including introducing drought-resistant crops, implementing recycling practices, adjusting fertilization methods, and adopting precision agriculture. Proposed alternatives encompassed regulatory measures and water rights reallocation. Additionally, students explored opportunities for expanding energy production without compromising water resource availability, considering alternative energy sources. They acknowledged that changes entail various trade-offs, eliciting diverse opinions and potential conflicts. Through these tasks, students compared their decisions with real scenarios. A student indicated
“I think there could always be more [water]. But GMOs make crops more drought resistant. So, the public must decide if they want organic stuff where it takes a lot more [water] or do they want GMOs where they can produce crops in arid regions” (interview S05 L145).
DISCUSSION
Understanding socio-hydrologic issues, such as the FEW nexus, requires honing undergraduate students’ systems thinking skills (Bajzelj et al., 2016; Davidson et al., 2021; Gilbert et al., 2019; Grohs et al., 2018; Platts et al., 2022; Redman & Wiek, 2021; Tsai & Liu, 2022). Learning experiences incorporating socio-hydrologic issues (Sabel et al., 2017) and other kinds of socio-scientific issues have been instrumental. This study utilized Hydroviz and a tailored assignment to evaluate a local issue within the FEW nexus framework, offering an ‘authentic complex Earth and environmental system’ perspective (Scherer et al., 2017). The findings contribute to understanding how course characteristics facilitate students’ understanding of socio-hydrologic issues and cultivate systems thinking and decision-making skills through authentic cases, and diverse data visualization and modelling tools (Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Lally et al., 2020; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2024; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; Owens et al., 2020; White et al., 2021).
Regarding the first and second research questions, “In what systems thinking constructs were students able to engage in most effectively?” and “In what ways do students with higher and lower scores differ?,” the analysis focused on part IV of the assignment. Like findings in prior studies (Liu, 2022), students exhibited moderate systems thinking average scores. Consistent with other research, students demonstrated greater proficiency in articulating the problem and the goals (Lally & Forbes, 2020; Liu, 2022). This outcome may be attributed to the structured questions in part IV serving as scaffolding for students’ understanding.
Results indicate the necessity for students to expand on constructs providing detailed analysis. Particularly, students exhibited lower evaluation regarding their information needs compared to other constructs (Grohs et al., 2018). Previous studies have highlighted challenges among students in critically evaluating the validity of various information sources (Owens et al., 2020) and integrating such information into their analysis (Sabel et al., 2017). Although socio-scientific issues involve having incomplete information, the ability to discern accuracy and identify needs for additional information is crucial for critical evaluation. This underscores the importance of reflecting on the significance of acquiring and integrating critical information when assessing socio-scientific issues. Regarding students’ analysis of different perspectives, most were proficient in identifying and characterizing stakeholders and their roles in the case. This aligns with findings from other studies where students effectively described stakeholders, analyzed their perspectives, and anticipated potential responses to issues (Owens et al., 2020; Platts et al., 2022; Redman & Wiek, 2021; Tsai & Liu, 2022) which is an important skill to cultivate to address complex issues (Davidson et al., 2021). However, students with lower scores had issues articulating the importance of stakeholders’ buy-in to solve the issue. Additionally, analyses of unintended consequences (Lally & Forbes, 2020) and implementation challenges (Liu, 2022) received lower scores among these students. Instructors might consider incorporating resources illustrating how diverse stakeholders contribute to identifying solutions to socio-hydrologic issues, along with highlighting the outcomes of such strategies. This approach could facilitate students’ deeper understanding of the significance of stakeholders’ buy-in while engaging with the assignment.
Students with higher scores demonstrated a better ability to incorporate contextual and technical aspects into their analysis, whereas students with lower scores tended to emphasize technical aspects over contextual ones (Grohs et al., 2018; Liu, 2022; Redman & Wiek, 2021; Scherer et al., 2017; Tsai & Liu, 2022). These results suggest that while students may find technical aspects more evident, integrating contextual aspects into their analyses may require additional support. Instructors could address this by directly prompting students to consider the social, political, and environmental implications (e.g., environmental justice) of the issues under study, fostering discussions and activities that encourage reflection on these aspects. Moreover, providing more contextual information about the regions being investigated could enhance students’ understanding, although this would require instructors to invest additional effort in creating cases and identifying suitable resources.
Regarding the third research question, “What factors support students’ systems thinking outcomes?,” the results showed a correlation between systems thinking scores and SSR. Research has shown the importance of developing students’ SSR to facilitate their engagement in decision-making about socio-hydrologic issues (Owens et al., 2020; Romine et al., 2017; Sadler et al., 2007; Tsai & Liu, 2022). Second, no clear relationship was observed between any demographic variable or any of the scores of the pre-assessment sections with students’ systems thinking scores, aligning with findings from Mostacedo-Marasovic and colleagues (2022). However, some studies have identified differences between groups of students in their analyses of other socio-scientific issues (Bajzelj et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2010; Platts et al., 2022). Instructors could support students by providing response exemplars that demonstrate analyses of different depths, helping to guide their own analyses.
While part IV of the assignment primarily focuses on the energy system and its connection with other systems, insights from the interviews shed light on how the tool and the assignment’s questions facilitated students in making connections between the FEW nexus systems in parts I, II, and III. This is significant as making such connections requires substantial cognitive processing, which tools like Hydroviz, coupled with effective instruction can help alleviate, thereby enhancing students’ systems thinking skills (Bajzelj et al., 2016; Davidson et al., 2021; Forbes et al., 2018; Lally & Forbes, 2020; Lally & Forbes, 2019; Lally et al., 2020; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022; White et al., 2021). To further support students in bridging their data analysis with their decision-making task, instructors could consider incorporating an additional question at the end of parts I, II, and III of the assignment prompting students to summarize their findings and main takeaways. Additionally, including a question at the beginning of part IV asking students to describe their region based on their previous findings could help set the stage for integrating their analyses into their decision-making process.
The asynchronous nature of the course during the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted students’ engagement with the assignment and Hydroviz. Feedback from interviews revealed varying experiences among participants, with some recognizing Hydroviz as a valuable tool for water-related learning but expressing the need for enhanced guidance, improved user interface, and more accessible instructional resources. This feedback aligns with findings from Mostacedo-Marasovic and colleagues (2022), who noted students’ recommendations for additional guidance and time for course activities. Liu (2022) also highlighted the effects of transitioning to an online asynchronous mode on student experience. It is also possible that due to time limitations or other constraints, some students might have preferred to limit their responses. While several efforts were made to maintain communication and support for students, it is important to encourage students to take advantage of them particularly in asynchronous settings (Davidson et al., 2021; Mostacedo-Marasovic et al., 2022).
Limitations
This study is limited in a number of ways. While research indicates the benefits of explicit instruction on systems thinking (Gilbert et al., 2019; Lally & Forbes, 2020), the module’s focus was on students’ learning about decision-making rather than directly teaching systems thinking. Still, students had exposure to water and human systems in previous course modules. Future adaptations could consider incorporating explicit instruction about systems thinking, recognizing the connection between environmental systems and human activities. Methodologically, the number of interviews conducted was limited. Future iterations could include additional questions to obtain responses about how the activity supported their learning about the systems, which could be evaluated alongside the interviews. Also, the first year of the project served as a pilot focused on module design and initial implementation, transitioning from in-person to online mode. This year was not included in the study. Further research is needed to assess any causal relationship between students’ online interaction skills and their learning achievements within module’s context. Pre- and post-measures specific to the module were not included in the study to evaluate students’ systems thinking skills. Future evaluations could incorporate such measures to assess learning gains. Moreover, students’ prior experiences were not detailed. Future research could include questions about students’ prior experiences with elements of the FEW nexus in demographic surveys and interview protocols to provide valuable insights.
CONCLUSIONS
The study contributes to understanding how students highlight distinct aspects of their systems thinking skills when assessing a socio-scientific issue focused on the FEW nexus. Hydroviz facilitated students’ access to data on water, energy, and agriculture patterns via a unique platform. The assignment questions acted as scaffolding, guiding students through diverse analyses to grasp these systems’ fundamentals for decision-making. However, effective usage of such tools requires proper guidance, particularly in asynchronous settings, to overcome potential challenges students may face independently. Furthermore, framing questions appropriately is essential for students to achieve desired learning outcomes. Therefore, the authors recommend incorporating additional questions tailored to areas where students may require improvement, facilitating deeper analyses. The study contributes to the literature on undergraduate students’ systems thinking within the realm of “authentic complex Earth and environmental systems” (Scherer et al., 2017). Although our evaluation focused on the FEW nexus, these resources hold potential for assessing various socio-scientific and complex issues beyond this scope.
Author contributions: S-JM-M & CTF: conception and design of the research project, the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, and the drafting and revision of the work & HCW: conception and design of the research project, the acquisition and analysis of data, and revision of the work. All authors agreed with the results and conclusions.
Funding: This study was supported by the National Science Foundation (DUE-IUSE # 1609598 and DUE-IUSE # 1726965) and the United States Department of Agriculture–National Institute of Food and Agriculture (grant # 2020-70003-35995, project accession # 1027670). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of these funding agencies.
Acknowledgments: The authors would like to thank Dr. Emad Habib, the reviewers, and the students for their contributions to better understand undergraduate education about water resources.
Ethical statement: The authors stated that the study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Texas at Arlington on 15 May 2023 with approval number 2021-0793.1.
Declaration of interest: No conflict of interest is declared by the authors.
Data sharing statement: Data supporting the findings and conclusions are available upon request from the corresponding author.
APPENDIX A: EXAMPLES OF QUESTIONS FROM THE FOUR-PART ASSIGNMENT
Part 1. Exploring Your Region
-
Water availability and stress
-
First, choose 2-4 adjoining HUC8s within your selected area.
-
Please list the names of the HUC8s you selected.
-
Click the “i” button and click on each HUC8 in your region. What is the total water availability in your region? (Note. Water availability = groundwater + surface water supply). So, add together for each HUC8: Mean annual flow plus groundwater recharge, show your work. How much total water is available for use in the region? Total water available for entire region =
-
Table A1. HUCs
|
-
What % of water available is surface water? What % is groundwater?
-
Click on the map button next to “HUC8 water data”, select the classification variables “mean annual flow” and “groundwater recharge”. Click the display each time you change the variable. How do HUC8s in your region vary in terms of water availability? Describe any variability you observe for both surface and groundwater.
-
Which areas or HUC8s in your region have high water availability? Record the names of the HUC8s here. Discuss both surface and groundwater availability.
-
Now select the classification variable “water stress ratio” and click display. How do HUC8s in your region vary in terms of overall water stress? Describe any trends and/or variability you observe.
-
Energy generation
-
Agriculture production
Part 2. Agriculture
-
Water for agriculture
-
Monetary value of agricultural production
-
Agricultural commodities
-
Water footprint of agriculture
-
Which counties are in your HUC8?
-
-
Look at USDA data: https://bit.ly/USDAData. Select your state, then Table A1. What kinds of livestock are produced in your HUC8?
-
Choose one livestock in your HUC8. How many are produced?
-
Convert livestock weight into kilograms.
1 cow: 550-600 kg
1 pig: 110-130 kg
1 sheep: 55-70 kg
1 goat: 30-45 kg
1 chicken: 2 kg
-
Please access the link: https://bit.ly/agwaterfootprint. Calculate the water footprint for this livestock in your region. How many m3 of water is being used to produce this livestock? 1 liter = 0.001 m3.
-
Land footprint of agriculture
-
Carbon footprint of agriculture
Part 3. Energy
-
Water and energy
-
Water footprint of energy
-
Land footprint of energy
-
Select one plant: What is its name? and what kind of energy does it produce?
-
How many MW does this plant generate?
-
How many acres of land is the plant you selected using?
-
Table A2. Land use by electricity source in acres/MW produced
| ||||||||||||||||
-
Energy production costs
Part 4. Decision-Making
-
Define the problem
-
Define objectives/criteria
-
Options vs criteria
-
Analyze the table
-
Explain why you chose the weights for each criterion. How did this fit with your objectives?
-
-
Which option is best for your highest weighted criteria? What are the drawbacks of this option?
-
Which options have the highest overall scores? What are the drawbacks of these options?
-
Did the table change your initial thoughts about any of the options?
-
Compare the options in as much detail as possible. What did you find when you looked at each criterion? What are the tradeoffs for each option?
-
Overall, what are the best options? Why?
-
Which options should be avoided? Why?
-
Make a decision
-
Review your decision
-
APPENDIX B: SYSTEMS THINKING CONSTRUCTS’ RUBRIC
Table B1. Systems thinking constructs’ rubric (adapted from Grohs, 2018 and Lally & Forbes, 2020)
|
APPENDIX C: SEGMENTS OF THE SEMI-STRUCTURED INTERVIEW PROTOCOL FOCUSED ON PARTS I, II, AND III OF THE ASSIGNMENT AND STUDENTS’ ENGAGEMENT WITH HYDROVIZ
Today is [date], I am interviewing [student name] about HydroViz. Thank you for participating in this interview. Over the past two weeks, you worked on a class assignment using HydroViz. Today, we are going to talk about your assignment and your experience using HydroViz.
In the assignment, you were presented with a scenario that you were asked to make a decision about in part four. This scenario involved a challenge in your region that was related to the use of water, energy generation, and agriculture production.
In part I of the assignment, you chose a single U.S. region and used HydroViz to explore water availability and use for energy generation and agriculture production.
-
Please share one or two main things you learned in this part of the assignment. What were your main takeaways?
-
Please, share with me how sustainably do you think water is being used in your selected region? Please explain your response using findings from your assignment.
-
How helpful was HydroViz for understanding the food-energy-water nexus?
In part II of the assignment, you used HydroViz to help you explore agriculture production and its use of water, its monetary value, the main commodities being produced, and its different types of footprints in your region.
-
Please share one or two main things you learned in this part of the assignment. What were your main takeaways?
-
Please, share with me how sustainably do you think water for agriculture production is being used in your selected region? Please explain your response using findings from your assignment.
-
How helpful was HydroViz for understanding the food-water nexus?
In part III of the assignment, you used HydroViz to help you explore energy generation and its use of water, its different types of footprints, and its production costs in your region.
-
Please share one or two main things you learned in this part of the assignment. What were your main takeaways?
-
Please, share with me how sustainably do you think water for energy generation is being used in your selected region? Please explain your response using findings from your assignment.
-
How helpful was HydroViz for understanding the energy-water nexus?
Finally, these are questions about the use of HydroViz itself:
-
What did you like about HydroViz? What are some things it helped you see and do?
-
What did you not like about HydroViz? What are some of its limitations?
-
If you could change HydroViz, what would you change to improve it?
APPENDIX D: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 4
Table D1. p-values of ANOVAs between demographic variables and systems thinking scores
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
APPENDIX E: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 5
Table E1. Correlations between pre-tests and systems thinking scores
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Bajzelj, B., Fenner, R. A., & Curmi, E. (2016). Teaching sustainable and integrated resource management using an interactive nexus model. International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 17(1), 2-15. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-02-2014-0022
- Choi, B. C. K., & Pak, A. W. P. (2006). Multidisciplinarity, interdisciplinarity and transdisciplinarity in health research, services, education and policy: 1. Definitions, objectives, and evidence of effectiveness. Clinical and Investigative Medicine, 29(6), 3351-364.
- Davidson, J., Prahalad, V., & Harwood, A. (2021). Design precepts for online experiential learning programs to address wicked sustainability problems. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 45(3), 319-341. https://doi.org/10.1080/03098265.2020.1849061
- FAO. (2014). The water-energy-food nexus: A new approach in support of food security and sustainable agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization. https://www.fao.org/3/bl496e/bl496e.pdf
- Forbes, C. T., Brozović, N., Franz, T. E., Lally, D. E., & Petitt, D. N. (2018). Water in society: An interdisciplinary course to support undergraduate students’ water literacy. Journal of College Science Teaching, 48(1), 36-42. https://doi.org/10.2505/4/jcst18_048_01_36
- Gilbert, L. A., Gross, D. S., & Kreutz, K. J. (2019). Developing undergraduate students’ systems thinking skills with an InTeGrate module. Journal of Geoscience Education, 67(1). 34-49. https://doi.org/10.1080/10899995.2018.1529469
- Grohs, J. R., Kirk, G. R., Soledad, M. M., & Knight, D. B. (2018). Assessing systems thinking: A tool to measure complex reasoning through ill-structured problems. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 28, 110-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2018.03.003
- Habib, E., Williams, D. C., Ma, Y., & Sharif, H. (2012). Hydroviz: Design and evaluation of a web-based tool for improving hydrology education. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 16, 3767-3781. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-3767-2012
- Lally, D., & Forbes, C. T. (2019). Modeling water systems in an introductory undergraduate course: Students’ use and evaluation of data-driven, computer-based models. International Journal of Science Education, 41(14), 1999-2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2019.1657252
- Lally, D., & Forbes, C. T. (2020). Sociohydrologic systems thinking: An analysis of undergraduate students’ operationalization and modeling of coupled human-water systems. Water, 12(1040). https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041040
- Lally, D., Franz, T., & Forbes, C. (2020). Undergraduate education about water and climate change: Students’ use of a water balance model. The Journal of Sustainability Education.
- Liu, S. -C. (2022). Examining undergraduate students’ systems thinking competency through a problem scenario in the context of climate change education. Environmental Education Research, 29(12), 1780-2795. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504622.2022.2120187
- Liu, S.-Y., Lin, C.-S., & Tsai, C.-C. (2010). College students’ scientific epistemological views and thinking patterns in socioscientific decision making. Science Education, 95(3), 497-517. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.20422
- Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2016). Qualitative data analysis. In S. B. Merriam, & E. J. Tisdell (Eds.), Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation (pp. 195-236). Jossey-Bass.
- Mostacedo-Marasovic, S. J., & Forbes, C. T. (2024). Faculty development program about the Food-Energy-Water Nexus: Supporting faculty’s adoption of a curricular module and program evaluation. International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 25(8), 1837-1853. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-06-2023-0262
- Mostacedo-Marasovic, S. J., Lally, D., Petitt, D. N., White, H., & Forbes, C. (2022). Supporting undergraduate students’ developing water literacy during a global pandemic: A longitudinal study. Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research, 4(7). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-022-00049-y
- Mostacedo-Marasovic, S. J., White, H. C., & Forbes, C. T. (2024). The Food-Energy-Water Nexus: Assessing undergraduate students’ decision making about complex socio-hydrologic issues supported by Hydroviz. Journal of Geoscience Education, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10899995.2024.2358726
- NRC. (2005). Decision making for the environment: Social and behavioral science research priorities. The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/11186
- Owens, D., Petitt, D., Lally, D., & Forbes, C. T. (2020). Cultivating water literacy in STEM education: Undergraduates’ socio-scientific reasoning about socio-hydrologic issues. Water, 12(2857). https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102857
- Platts, E. J., Kerner, B., Adams, A. & Archer, J-A. (2022). Rebalancing research and training priorities at the food-energy-water nexus. Science and Education, 31, 1383-1397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11191-022-00344-0
- Redman, A. & Wiek, A. (2021). Competencies for advancing transformations towards sustainability. Frontiers in Education, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2021.785163
- Rittel, H. W., & Webber, M. M. (1973). Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sciences, 4, 155-169. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01405730
- Romine, W. L., Sadler, T., & Kinslow, A. T. (2017). Assessment of scientific literacy: Development and validation of the quantitative assessment of socio-scientific reasoning (QuASSR). Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 54(2), 274-295. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.21368
- Sabel, J., Vo, T., Alred, A., Dauer, J., & Forbes, C. (2017). Research and teaching: Undergraduate students' scientifically informed decision making about socio-hydrological issues. Journal of College Science Teaching, 046(06). https://doi.org/10.2505/4/jcst17_046_06_71
- Sadler, T. D., Barab, S. A., & Scott, B. (2007). What do students gain by engaging in socioscientific inquiry? Research in Science Education, 37, 371-391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-006-9030-9
- Scherer, H. H., Holder, L., & Herbert, B. (2017). Student learning of complex Earth systems: Conceptual frameworks of Earth systems and instructional design. Journal of Geoscience Education, 65(4), 473-489. https://doi.org/10.5408/16-208.1
- Tsai, J.-C. & Liu, S.-Y. (2022). Implementing the instructional model of socioscientific board game in a general education course. In Y.-S. Hsu, R. Tytler, & P. J. White (Eds.), Innovative approaches to socioscientific issues and sustainability education: Linking research to practice (251-271). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1840-7
- USDA–NASS. (2018). Census of agriculture 2017: Data and statistics. United States Department of Agriculture–National Agricultural Statistics Service. https://www.nass.usda.gov/Data_and_Statistics/index.php
- Wade, A. A., Grant, A., Karasaki, S., Smoak, R., Cwiertny, D., Wilcox, A. C., Yung, L., Sleeper, K., & Ananthi, A. (2020). Developing leaders to tackle wicked problems at the nexus of food, energy, and water systems. Elementa Science of the Anthropocene, 8, Article 11. https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.407
- White, H., & Forbes, C. T. (2021). An investigation of undergraduate students’ spatial thinking about groundwater. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 47(1), 128-148. https://doi.org/10.1080/03098265.2021.2004582
How to cite this article
APA
Mostacedo-Marasovic, S.-J., White, H. C., & Forbes, C. T. (2025). The food-energy-water nexus: Using Hydroviz to support undergraduate students’ systems thinking about complex socio-hydrologic issues. Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 21(2), e2506. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901
Vancouver
Mostacedo-Marasovic SJ, White HC, Forbes CT. The food-energy-water nexus: Using Hydroviz to support undergraduate students’ systems thinking about complex socio-hydrologic issues. INTERDISCIP J ENV SCI ED. 2025;21(2):e2506. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901
AMA
Mostacedo-Marasovic SJ, White HC, Forbes CT. The food-energy-water nexus: Using Hydroviz to support undergraduate students’ systems thinking about complex socio-hydrologic issues. INTERDISCIP J ENV SCI ED. 2025;21(2), e2506. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901
Chicago
Mostacedo-Marasovic, Silvia-Jessica, Holly C. White, and Cory T. Forbes. "The food-energy-water nexus: Using Hydroviz to support undergraduate students’ systems thinking about complex socio-hydrologic issues". Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education 2025 21 no. 2 (2025): e2506. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901
Harvard
Mostacedo-Marasovic, S.-J., White, H. C., and Forbes, C. T. (2025). The food-energy-water nexus: Using Hydroviz to support undergraduate students’ systems thinking about complex socio-hydrologic issues. Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 21(2), e2506. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901
MLA
Mostacedo-Marasovic, Silvia-Jessica et al. "The food-energy-water nexus: Using Hydroviz to support undergraduate students’ systems thinking about complex socio-hydrologic issues". Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, vol. 21, no. 2, 2025, e2506. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15901

 Full Text (PDF)
Full Text (PDF)